-
Biopsy: ≥ 10 specimens from the base of the ulcer. ∆+: Histology identification of CMV by immunohistochemical and direct fluorescence staining
-
Blood test : antigen, viral culture, PCR
-
Others test: Immunodeficiency, renal failure, malignancy, transplanted organs, HIV, steroid or immunosuppressive therapy
-
Treatment: Treatment primary disease: immunodeficiency… Antivirus: Ganciclovir/forcarnet IV, oral Valganciclovir
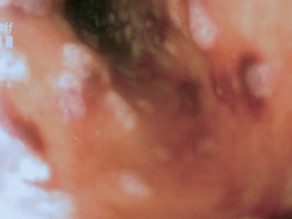
Cytomegalovirus esophagitis
Lesion: Esophageal ulceration and vasculitis caused by CMV infection at multiple sites
Related posts
- Normal esophagus - 03-05-2021
- Zenker's diverticulum (zd) - 29-04-2021
- Esophageal webs - 03-05-2021
- Gastric inlet patches in esophagus (heteropic gastric mucosa of the proximal esophagus) - 03-05-2021
- Esophageal glycoenic acanthosis - 03-05-2021
- Benign and malignant esophageal tumors - 03-05-2021
- Esophageal varices and sarin's classification for gastric varices - 03-05-2021
- Mallory - weiss tear - 03-05-2021
- Typical findings of primary esophageal achalasia - 03-05-2021
- Esophageal stenosis - 03-05-2021
EDUCATION
-

Self-design suction tool
20-05-2021 -

Removing phytobenzoar in Pig's stomach
20-05-2021 -

Remove twisting of the pig colon
04-05-2021 -
Pig stomach endoscopy
04-05-2021
Recommendation
-

Management of Ingested Foreign Bodies in Children: A Clinical Report of the NASPGHAN Endoscopy Committee
28-04-2021 -

Management of Familial Adenomatous Polyposis in Children and Adolescents: Position Paper From the ESPGHAN Polyposis Working Group
28-04-2021 -

Pediatric Colonoscopic Polypectomy Technique
28-04-2021 -

Gastrostomy Placement in Children: Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy or Laparoscopic Gastrostomy?
28-04-2021
Videos
Contact







