Esophageal stenosis
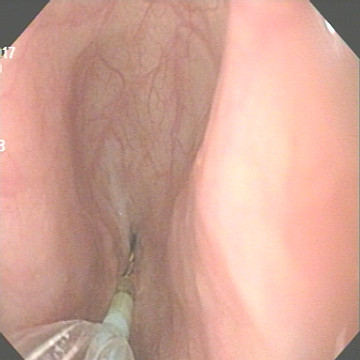
Lesion: Esophageal stenosis (1mm of diameter) at 4cm from upper sphincter and 13cm from front teeth, straight shaft, no oedema, no diverticula, no fistula in the boy 2-year-old operated esophagael astresia
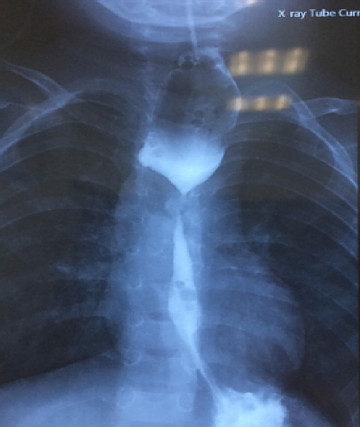
X ray: Esophageal stenosis located at the D4, straight shaft, no diverticula, no fistula. Large esophagus on upper stenosis
Initial Management
• Barium esophagram radiology
• CT scan Δ ≠: Congenital or extrinsic esophageal stricture
• Treatment:
– Endoscopy: Esophageal dilatation ± intralesional steroid injection, Mytomycin C, stent
– Surgery: Esophageal anatomosis or replacement of the esophagus (by stomach or colon)
Related posts
- Normal esophagus - 03-05-2021
- Cytomegalovirus esophagitis - 04-05-2021
- Zenker's diverticulum (zd) - 29-04-2021
- Esophageal webs - 03-05-2021
- Gastric inlet patches in esophagus (heteropic gastric mucosa of the proximal esophagus) - 03-05-2021
- Esophageal glycoenic acanthosis - 03-05-2021
- Benign and malignant esophageal tumors - 03-05-2021
- Esophageal varices and sarin's classification for gastric varices - 03-05-2021
- Mallory - weiss tear - 03-05-2021
- Typical findings of primary esophageal achalasia - 03-05-2021
EDUCATION
-

Self-design suction tool
20-05-2021 -

Removing phytobenzoar in Pig's stomach
20-05-2021 -

Remove twisting of the pig colon
04-05-2021 -
Pig stomach endoscopy
04-05-2021
Recommendation
-

Management of Ingested Foreign Bodies in Children: A Clinical Report of the NASPGHAN Endoscopy Committee
28-04-2021 -

Management of Familial Adenomatous Polyposis in Children and Adolescents: Position Paper From the ESPGHAN Polyposis Working Group
28-04-2021 -

Pediatric Colonoscopic Polypectomy Technique
28-04-2021 -

Gastrostomy Placement in Children: Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy or Laparoscopic Gastrostomy?
28-04-2021
Videos
Contact







