Phan Thi Hien, "Esophagus-stomach-duodenum endoscopy in children", Medical Publishing House, Hanoi, Jan 2019 (page 21-33). Extract from specialty book: “NỘI SOI THỰC QUẢN – DẠ DÀY – TÁ TRÀNG TRẺ EM”, Nhà xuất bản y học, Hà Nội, ISBN: 978-604-66-3546-8.
INTRODUCTION
With the rapid development of technology, gastrointestinal endoscopes were invented, which marked a milestone in the evolution of the gastroenterology field. It is important to understand the function, the way to use and select the appropriate endoscope for the patients.
EQUIPMENTS
1.1. Types of endoscope
Classification on the basic of image transition:
- Video endoscope (endoscope recording by camera).
- Fiber-optic endoscope (endoscope recording by optical fiber).
Classification on the basic of function of viewing:
- Forward viewing endoscope (gastroscope, colonoscope and enteroscope): used for upper and lower gastrointestinal endoscopy (ileocolonoscopy) and enteroscopy.
- Side-viewing endoscope: used for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic ultrasonography.
With the development of medical equipment manufacturers, the smallest endoscopes appeared for infants from over 1200g body of weight [1]. In clinical practice, the gastroscopes have various sizes to be suitable for different ages:
- Small endoscopes usually have an outer diameter of 5.5 mm which are used for gastrointestinal endoscopy on the newborn and the children under 2years old. This endoscope has only one channel for biopsy and air/water, mainly used for diagnostic endoscopy.
- Bigger endoscopes have separated two channels with biopsy channel and air/water channel. These endoscopes with outer diameter of 7.9 mm are used for children from 2 to 7 years old with a working channel of 2mm, mainly used for diagnostic endoscopy.
- Standard endoscopes are used for the children more than 7 years old and the adults have a working channel of 2.8mm with the larger outer diameter [1]. This type of endoscope is mostly used in intervention.
In 2017, The European society for Pediatric Gastroenterology-Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) in collaboration with the European Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) has issued the following recommendations for upper gastrointestinal endoscopy in children: under 10 kg body of weight or under 1 year old should use the endoscopes with an outer diameter ≤ 6 mm for diagnostic endoscopy and standard gastroscopes for interventional endoscopy; for older children, the standard endoscopes always be used [2]. However, in some special cases such as gastrointestinal stenosis, ulceration of the gastrointestinal tract, small endoscopes are preferred even in older children.
The study of Phan Thi Hien et al showed that a standard gastroscope is safe for children from 5 years old, without causing gastrointestinal injury [3]. In 2008, Phan Thi Hien et al reported a 2-month-old girl weighing 2.8 kg had duodenal stenosis after surgery who successfully underwent anastomotic dilatation by standard gastroscope, no complications [4]. However, the big endoscope is used for small and low weight patients and the technique should be performed gently and carefully.
Another report by Phan Thi Hien et al in 2017 shows standard gastroscope with a 2.8mm working channel was safe and effective for interventional endoscopy to stop bleeding with clips on two low weight infants after cardiac surgery. In both cases, the endoscope with a 2mm working channel was not unable to clean the gastrointestinal tract because there were a lot of blood clots and to use clip [5].
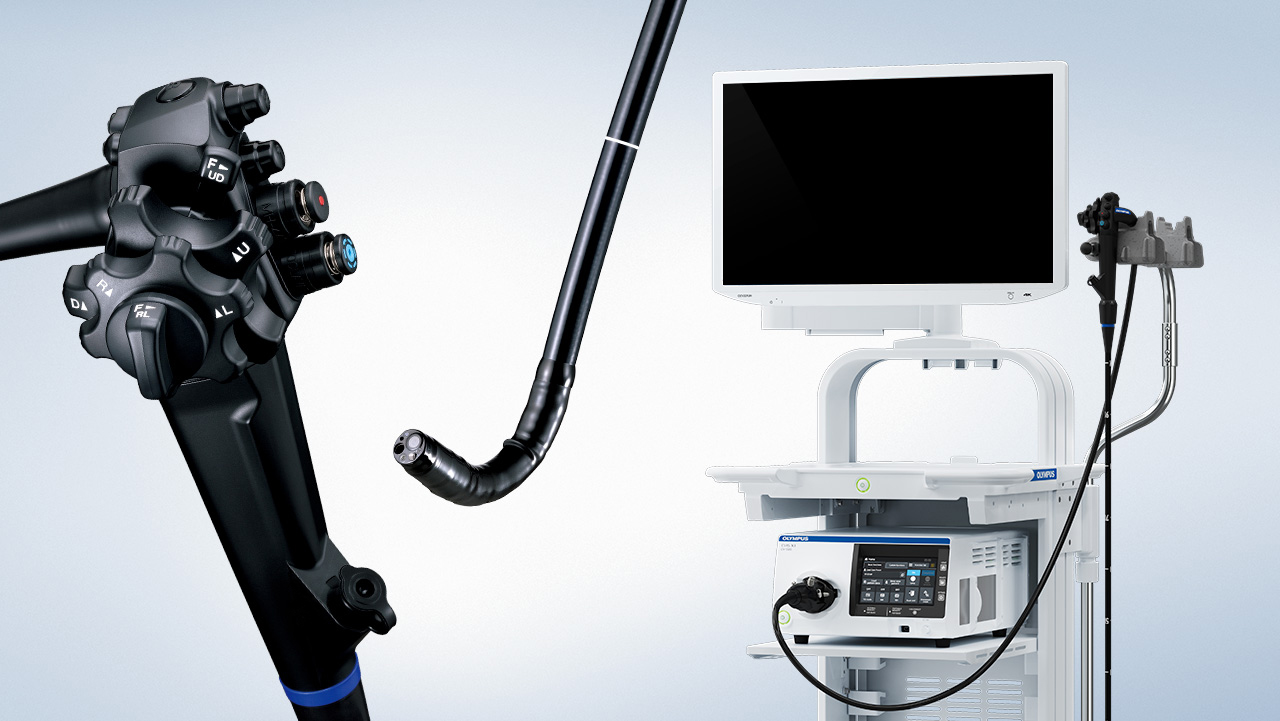
1.2. Structure of endoscope
Outer structure of endoscope
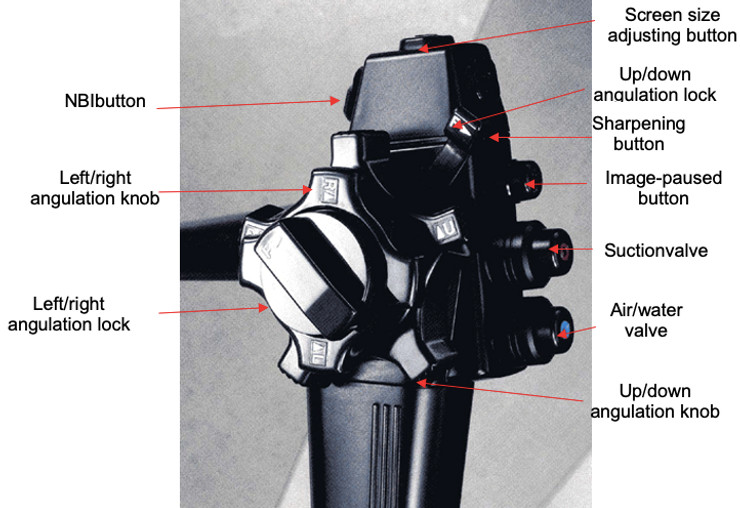
How to use valves and buttons:
- Suction: press the suction valve by finger.
- Pumping air: cover the air-water valve by finger.
- Pumping water: press the air-water valve by finger.
- Only one valve for pumping air and water.
- The 2 parts of the biopsy valve: the fixed part and the removable part. The fixed part is not removed within biopsy.
- NBI button (narrow-band imaging) only works for endoscopes with this mode, the light is turned green to improve the image visibility of blood vessels, so the biopsy will be more exactly on the position suspected cancer (due to vascular proliferation images).
How to use the angulation knobs:
- The up-down angulation knob has the function of moving the direction of the end of endoscope to up or down. Using:
+ To move the end of the endoscope up, use the left thumb to move the up angulation knob counterclockwise.
+ To move the end of the endoscope down, use the left thumb to move the down angulation knob clockwise.
- The left-right angulation knob has the function of moving the direction of the end of the endoscope to the right or the left. Using:
+ To move the end of the endoscope to the right, use the left thumb to move the right angulation knob clockwise.
+ To move the end of the endoscope to the left, use the left thumb to move the left angulation knob counterclockwise.
When adjusting the angulation knob do not use extreme movements, because the chains can be easy to stretch and break, especially the up-down wheel due to heavy use. Do not lock the angulations when the endoscope is working, only use the lock when needing the end of the endoscope to be in a fixed position for special techniques.

The bending part
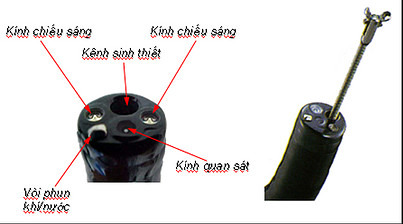
Distal tip of endoscope
- Universal cord includes: Fiber optic bundle for light, air and water channel, suction channel and electric line for intervention.

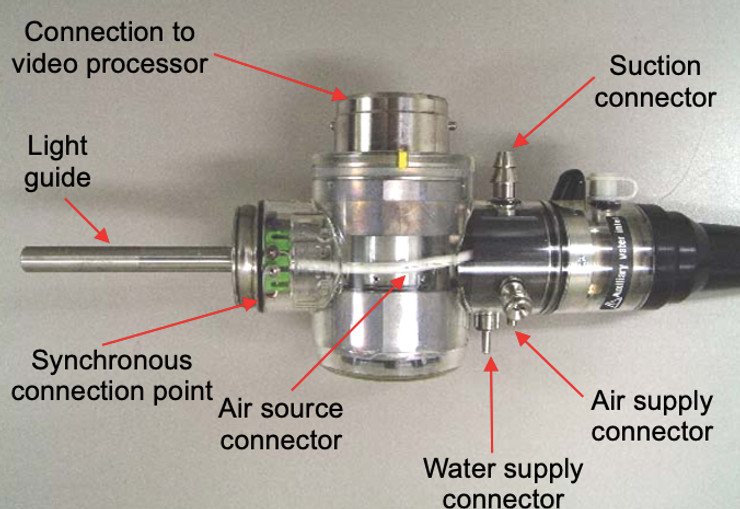
Insertion tube of an endoscope and the universal cord
- Light source connector: Light guide, air pipe, S-Cord connector, suction connector, venting cap connector, air and water supply connector.
1.3. Internal component and construction of endoscope
Flexible endoscopes without video use fiber optical cables. These fiber bundles contain cylinders made by material with a low refractive index. Each fiber is made of coated glass as a mirror that reflects the light through the optical fibers into the eye when the light enters to the end of the optical fibers [6].
Flexible endoscopes with video, the principle is the same as an endoscope without video which uses fiber optic cables. However, these optical fibers are only capable of light transmitting but not images. The transmission of images is due to an objective lens through an unit called CCD (charge Coupling Device - chip) is attached to the distal end of the endoscope and transmits images by electrical signals obtained from the camera.The CCD unit receives images from gastrointestinal mucosa and increases the quality of the image. The images captured by the camera are transmitted to the image processing unit and transferred to the screen [7].
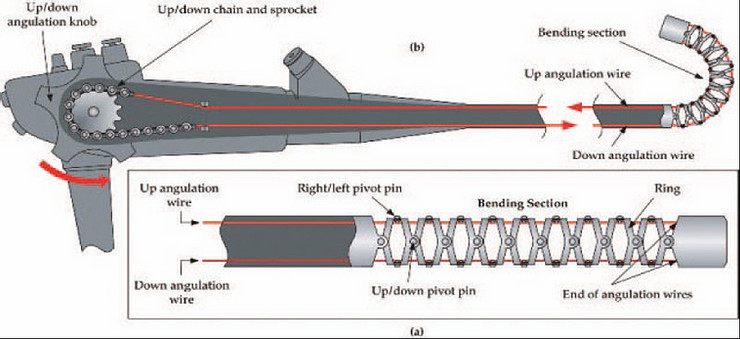
In addition, inside the device, there is an angulation system that controls the distal tip of the endoscope with the bending section of the endoscope, moved in four directions: up, down, left, right.
The light source compatible with each type of endoscope will provide light for the endoscope (normal light or cold light) and channel system to pump air and water. The upper gastrointestinal endoscope is a straight-view type, with 4-direction control system, allowing the entire upper gastrointestinal mucosa to be observed from the mouth to D2, D3, and the retro endoscopy in fundus, lesions are sometimes observed at the angle of Treitz, even the first segment of the jejunum. The light source is used for normal light with halogen lamp or cold light with xenon lamp, the light is automatically adjusted to ensure sufficient focus or manually adjusted to ensure optimal light [6, 7].
1.4. Technical features of some common endoscopes on children
Flexible endoscopes have different characteristics. Video endoscope was invented with many advantages such as creating beautiful images, less affected by the outside impact, more compact and quickly controlled the market. In Vietnam, endoscopic equipment manufacturers such as Olympus, Pentax, Fujinon, ... have different advantages and disadvantages.

Endoscopic accessories
Endoscopic accessories include canuyn, biopsy valve, air/water valve, suction valve, short brush, long brush, halogen or xenon lamp, manual endoscope washing and pumping kit, biopsy forcep, polyp snare, foreign body forcep, hemostatic needles ...
Biopsy forceps have teeth to clamp the mucosa. However, some biopsy forceps have a central needle that provides fixed and slip-resistant effect during biopsy [6] and helps perform multiple biopsies with one put forceps.



Canuyn with cord

Washing brush

-

Self-design suction tool
20-05-2021 -

Removing phytobenzoar in Pig's stomach
20-05-2021 -

Remove twisting of the pig colon
04-05-2021 -
Pig stomach endoscopy
04-05-2021
-

Management of Ingested Foreign Bodies in Children: A Clinical Report of the NASPGHAN Endoscopy Committee
28-04-2021 -

Management of Familial Adenomatous Polyposis in Children and Adolescents: Position Paper From the ESPGHAN Polyposis Working Group
28-04-2021 -

Pediatric Colonoscopic Polypectomy Technique
28-04-2021 -

Gastrostomy Placement in Children: Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy or Laparoscopic Gastrostomy?
28-04-2021







