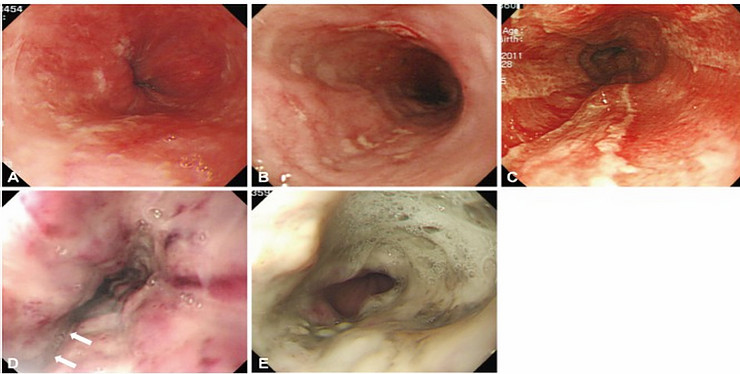
Zagar classification for corrosive ingestion
Park KS, Evaluation and Management of Caustic Injuries from Ingestion of Acid or Alkaline Substances, Clinical Endoscopy 2014; 47(4): 301-307 De LusongMA, Management of esophageal caustic injury, World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther, 2017 May 6; 8(2): 90–98
(A) Grade 1 indicates only slight swelling and redness of the mucosa.
(B) Grade 2A indicates the presence of superficial ulcers, bleeding, and exudates.
(C) Grade 2B indicates local or encircling deep ulceration.
(D) Grade 3A indicates focal necrosis. White arrows indicate focal necrosis.
(E) Grade 3B indicates extensive necrosis.
Initial treatment
•Medicine: Corticoid, PPI, antibiotic depending on grade
•Intravenous dexamethasone at high dose (1 g/1.73 m2 per day) for 3 days in IIb esophagitis
•Esophageal dilatation or surgery for stricture
Related posts
- Normal esophagus - 03-05-2021
- Cytomegalovirus esophagitis - 04-05-2021
- Zenker's diverticulum (zd) - 29-04-2021
- Esophageal webs - 03-05-2021
- Gastric inlet patches in esophagus (heteropic gastric mucosa of the proximal esophagus) - 03-05-2021
- Esophageal glycoenic acanthosis - 03-05-2021
- Benign and malignant esophageal tumors - 03-05-2021
- Esophageal varices and sarin's classification for gastric varices - 03-05-2021
- Mallory - weiss tear - 03-05-2021
- Typical findings of primary esophageal achalasia - 03-05-2021
EDUCATION
-

Self-design suction tool
20-05-2021 -

Removing phytobenzoar in Pig's stomach
20-05-2021 -

Remove twisting of the pig colon
04-05-2021 -
Pig stomach endoscopy
04-05-2021
Recommendation
-

Management of Ingested Foreign Bodies in Children: A Clinical Report of the NASPGHAN Endoscopy Committee
28-04-2021 -

Management of Familial Adenomatous Polyposis in Children and Adolescents: Position Paper From the ESPGHAN Polyposis Working Group
28-04-2021 -

Pediatric Colonoscopic Polypectomy Technique
28-04-2021 -

Gastrostomy Placement in Children: Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy or Laparoscopic Gastrostomy?
28-04-2021
Videos
Contact







